As your website gets bigger, pagination SEO creeps up more in conversation.
And it’s understandable. A good pagination strategy can improve website speed, crawl budget efficiency, and link equity distribution.
Each and every one of these benefits can move the needle on your website. A needle that could result in higher rankings, more traffic, and ultimately, more customers.
What is Pagination in SEO?
Pagination is an SEO/design technique when pages (normally with related content) are organised into a sequential series.
Mostly, these pages use elements such as links or numbered buttons. Users can then click on these elements and move through the content archive.
Examples of Pagination SEO
One of the main examples of pagination is from a blog section. On our website, we use numbers. Users can then click these numbers to go through our content archive.
Another example of pagination SEO is from e-commerce shops. They use pagination to limit the number of items on one page and split them across several pages.
Just so you have a better idea of pagination, you can also find them on product reviews, forum pages, blog comments, and so on.
Types of Pagination Formatting
When it comes to pagination, you have three formatting choices. These are basic pagination, load more, and infinite scroll.
Basic Pagination
Basic pagination is the most used (and best) option. It follows a button format. For example, a user can click on buttons “1”, “2”, or “3” to go through a content archive of a blog. It’s the most simple and also provides the best user experience.
Load More
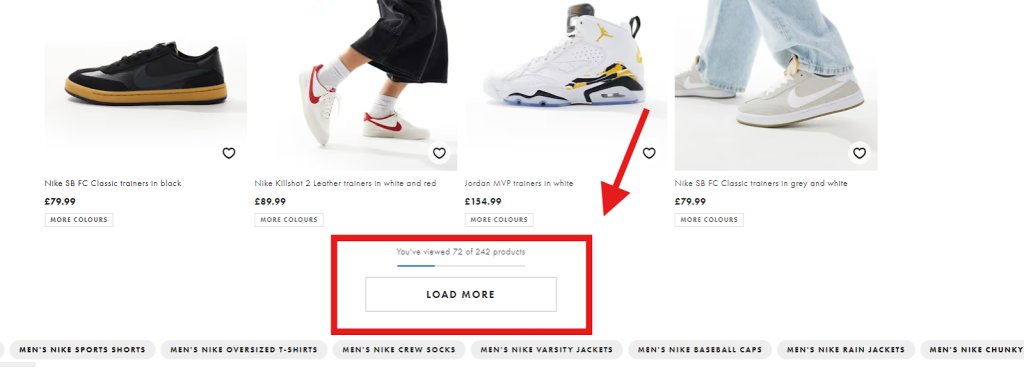
Unlike basic pagination, which uses buttons, load more has a big “Load More” button users need to click to expand the content of a page.
With load more, sometimes content can be pushed too deep into the site’s architecture. The recommended crawl depth is 3, but load more can push content 4, 5, or even 6+ deep.
Infinite Scroll
Infinite scroll is another type of pagination formatting. Think of “YouTube Shorts” or “TikTok”; instead of clicking “Load More” or buttons, scrolling automatically brings up new content.
It has a few pros and cons. The pro is that it keeps users engaged. A big con is that it’s not a good user experience, especially if they want to reach the footer of a website.
Is Pagination Good or Bad for SEO?
Pagination gets a lot of love and hate in the world of SEO.
One of the main issues around pagination and SEO is thin and duplicate content. However, neither of these issues is a problem that cannot be fixed.
You can easily avoid duplicate content by just using canonical tags. We go into more detail about this below.
For thin content, some thin content is okay, for example, on a contact or location page. However, if you have thin content on, let’s say, a landing page or blog post, then you’ll just need to add content.
With that said, pagination does have some benefits. Firstly, it’s great for bots and indexability. Secondly, it increases your digital real estate as you’ll have more pages online. Thirdly, it improves website speed.
Pros and Cons of Pagination SEO
When done right, pagination can present some great SEO benefits. But it also has its risks. Let’s take a look at both.
Pros
1. Improved UX
From a user’s perspective, pagination is great. It allows them to move through lots of content effortlessly.
Not only that, it tells the user where they are. For example, if they’re on “Page 3” of the blog content archive, they can see how many pages they have left “Page 4”, “Page 5”, and “Page 6”, etc.
2. Faster Page Loading Speed
Page speed is a huge ranking factor on search engines like Google. It’s no hidden secret. However, pagination splits the content over multiple pages, reducing loading resources and increasing loading speed.
3. Internal Linking Opportunity
Pagination can also link your website together via internal linking. This isn’t only good for crawling and indexing, but it’s also good for passing authority through your website.
It also pushes pages up in the site’s architecture. It shouldn’t be deeper than a crawl depth of 3. Therefore, by internal linking, you can push the content up, increasing the chances of it being crawled and indexed.
Cons
1. Duplicate Content
Duplicate content appears when a website has the same content on multiple pages. This only occurs from pagination if the site owner(s) set up pagination incorrectly.
For example, let’s say you have a “View All” button next to your paginated pages. The same content will appear on the “View All” page and the paginated pages, resulting in duplicate content.
2. Reduced User Engagement
If you don’t set up pagination while thinking about your users, it may result in reduced user engagement. It should benefit the user and not only be used for SEO purposes.
Pagination SEO Best Practices
1. Make Your Anchor Links Crawlable
If search engines cannot access your pagination pages, it’s a waste of time. They need to be able to crawl your pages to index them.
A common belief is that you don’t want pagination pages to rank, so many “noindex” them. However, you want them indexed.
But what about keyword cannibalisation? You can de-optimise your paginated pages. You don’t want them to compete with the root page.
You can do this by adding the page number to the meta title. For instance, “Page Two of XX Blog”. This is usually enough to indicate to search engines that this isn’t the root page.
2. Avoid Using a “View All” Page for Pagination
Sometimes, websites have a “View All” button, which will direct the user to see all of the content for a specific category. For instance, “View All” blog posts on a website.
This can cause a few problems. Firstly, it’ll be a slow page, especially if there’s a lot of content. Secondly, it gives the user too many options, providing a poorer user experience. Thirdly, it can, if you use basic pagination also, cause duplicate content.
Please note: “View All” can be good for websites with very little content. However, for large websites, this isn’t a good idea.
3. Use Self-Referencing Canonical Tags
Canonical tags suggest the preferred page on a website to search engines. It’s normally found in the <head> section of a webpage and is structured like:
- “<link rel=”canonical” href=”https://example.com/preferred-url-here/”/>”
Using canonical tags on paginated pages tells search engines, “This is the primary webpage for this content, regardless if it’s found elsewhere”.
Without it, search engines would have a difficult time understanding which is the primary page. As a result, it’ll end up not ranking any of the pages, as it’s unsure which one to rank.
For that reason, you want to use canonical tags for each paginated page. It’ll help search engines rank the right page and also avoid duplicate content.
4. Use URLs Properly
When it comes to URLs, make sure they’re clear. For example, here’s how paginated blog pages would look like:
- https://example.com/blog
- https://example.com/blog/?page=2
- https://example.com/blog/?page=3
Remember, don’t use URL fragment identifiers. These look like this:
- https://example.com/blog/#page2
See the difference? There’s a “#” and no “=”. This is what a fragment identifier looks like. However, Google ignores fragment identifiers, meaning your paginated pages might not be crawled.
5. Think of Pagination Pages like Internal Linking
Pagination SEO shouldn’t be complicated. It should just be looked at as internal linking. Nothing else than that.
As a result, use the same best practices:
- Link to relevant pages.
- Give users an idea of where they’re going.
- Don’t use too many links on a single page.
- If possible, target relevant keywords.
- Make sure no page is too deep in the site architecture.
By following these tips, you’ll be able to get a lot more from your paginated pages.
Final Word
After reading the above, you know everything to do with pagination SEO.
Though it’s more suited for those with large websites, if you plan to have a large website, having a solid pagination strategy now can help you in the future.
Alongside this, a site audit should be performed regularly on paginate pages. There are various tools for this, but you’ll want to audit crawl depth, duplicate content issues, and canonical tags.
Adding this to your technical audit list is hugely beneficial for your users and your SEO rankings and traffic.