On-page SEO is optimizing a webpage for search engines and users.
Search engines like Google analyze the page’s content to see if it matches a user’s search intent. If the search engine finds the helpful page, it will likely be shown higher in search results page (SERP).
Read this complete guide on on-page SEO importance because it emphasizes creating content that prioritizes the user experience, which is crucial for ranking well in search engines and your overall digital marketing strategy.
Want to get straight to it? Here’s the on-page SEO checklist I created to help implement on-page SEO techniques.
On-Page SEO Vs Off-Page SEO?
Many people need clarification about the difference between on-page and off-page SEO.
On-page SEO is anything you can do to improve your ranking in search engines.
On the other hand, off-page SEO is focused on optimizing your website outside of your control (for example, by using well-known social media platforms or digital PR) to boost your ranking in search engine results pages.
These two tactics are critical for any good SEO strategy, but as with most things in life, you have more control over on-page SEO ranking factors.
This means optimizing those aspects of your site that have the most impact will generally yield better results than working on off-page SEO factors and items that you may have less control over (for example, copywriting or technical issues).
| Aspect | On-Page SEO | Off-Page SEO |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Techniques you can apply directly on your website to improve search rankings. | Strategies focused on improving your website’s reputation and authority through external means. |
| Control Level | High control over these factors, as they are directly related to your site’s content and setup. | Less control, as it depends on external factors like backlinks, social media presence, and other off-site activities. |
| Key Focus | Optimizing content, improving site structure, enhancing user experience. | Link building, increasing social media engagement, and developing digital PR campaigns. |
| Examples | Adjusting meta tags, creating quality content, optimizing website speed and mobile responsiveness. | Earning backlinks from reputable sites, social media marketing, and influencer collaborations. |
| Impact | Directly affects how search engines view and rank your website. | Influences how your site is perceived externally, which indirectly affects search engine rankings. |
Why Is On-Page SEO Important?
There is no question that Google pays close attention to on-page SEO elements when ranking pages.
This is one of the reasons why focusing “Helpful, Reliable, People-First Content”is so important for optimal organic visibility.
Google famously crawls the web to figure out what pages are being indexed and ranked.
Once search engine crawlers understands the contents of a web page, it uses several algorithms (known as the’s) to determine how relevant that page is to the user and whether it should be served up in response to a search request.
However, even with all this data, Google prioritizes user experience over any other factor when ranking pages.
This means that if you want users to find and read your content, it must be valuable and relevant to your target audience.
So, while on-page SEO may not be as important as some think, it definitely cannot be ignored when evaluating the strength of your search engine optimization growth.
The TLDR for On-Page SEO
Here are some key on-page optimization techniques you should consider:
- SEO-Friendly URL Structure: Your website URLs should be like a precise, descriptive address, guiding people and search engines directly to your content.
- Target Keywords Purposefully: Select keywords strategically, ensuring they align with what your audience searches for and what your content offers.
- Write Unique, Helpful Content: Create original and useful content, providing valuable information or solutions to your visitors.
- Create Smart Title Tags: Craft title tags that capture attention and accurately describe what each web page is about.
- Write Enticing Meta Descriptions: Compose compelling meta descriptions that give a preview of your page’s content, encouraging clicks from search results.
- Internal Linking Strategy: Use hyperlinks to connect your web pages, guiding visitors to more relevant content and enhancing site navigation.
- External Linking Strategy: This involvesselectively linking to authoritative and relevant websites from your content to enhance its credibility and provide additional value to your readers.
- Target Featured Snippets: Optimize your content to fit into featured snippets, offering quick and direct answers to users’ search queries.
- Mobile-Friendly Website: Ensure your website is accessible and user-friendly across all devices, from desktops to mobile phones.
- Site Speed: Focus on a fast-loading website, providing visitors with a smooth and efficient experience.
- Add Schema Markup: Implement schema markup to help search engines better understand and display your content, enhancing its appearance in search results.
Let’s dive into these critical SEO topics one by one, breaking them down into simple concepts:
1. Target Keywords Purposefully
Keywords are like clues that tell search engines what your content is about.
Keyword research is choosing relevant keywords and topics to write about for a website.
This can be a daunting task, and there are many keyword research tools and methods to choose from that show keyword difficulty, search volume, and user intent.
Choose words that people use when they search for something you offer.
For instance, if you sell eco-friendly bags, keywords like “sustainable handbags” can help the right people find your website, and the type of traffic from search engines will lead to more engagement.
Appearing in relevant search results is more beneficial than having irrelevant organic traffic.
Including your target keywords in specific web page areas is crucial for search engines and users. Here’s a breakdown of where to place them:
- Page URL: Including your target keyword in the URL indicates your page’s content, enhancing relevance and user click-through in search results.
- H1 Tag: Placing your target keyword in the main headline immediately signals the main topic to both Google and visitors.
- First Paragraph: Adding your target keyword (fat head keywords) in the first paragraph immediately reinforces your page’s topic, aiding Google’s understanding and engaging your readers.
- Subheaders (H2s, H3s, etc.): Using keywords in subheaders organizes your content clearly, aiding Google’s interpretation and helping users find relevant information.
- Body Content: Through the on-page content, add in middle-chunky and long-tail keywords, these will help with semantic SEO.
2. SEO-Friendly URL Structure
Think of a page URL like the address of a house.
It helps people and search engines find your web page. A good URL is clear and descriptive, showing what the page is about.
For example, a URL like “www.flowershop.com/roses” tells you and search engines that the page is about roses.
When starting a brand new site, spending time after the keyword research phase to map out an ideal and SEO-friendly URL structure is a must-do for on-page SEO optimization.
Technical optimization for SEO may require re-evaluating your URL structure and changing it to match search terms through 301 redirects.
Optimized URLs are about making them clear and relevant to your content, which helps both Google and users understand your page better. Here are some key points:
- Use Relevant Keywords: Choose keywords for your URL that reflect your page’s content, making it easy for users to guess what the page is about just by looking at the URL.
- Avoid Random Numbers and Dates: Avoid using non-descriptive numbers, dates, or long sentences in your URL. These can make the URL confusing and less helpful for users and search engines.
- Update Default URLs: Website themes might generate default URLs that aren’t very descriptive. Always customize your URL to make it more relevant before publishing.
- Include Long Tail Keywords: Adding your long tail keyword in the URLs structure ensures you can rank for more search terms that will bring in additional organic traffic.
- Friendly URL Examples: Compare an unfriendly URL filled with random characters to a friendly one with clear, relevant words. The difference will show how user-friendly and understandable the latter is.
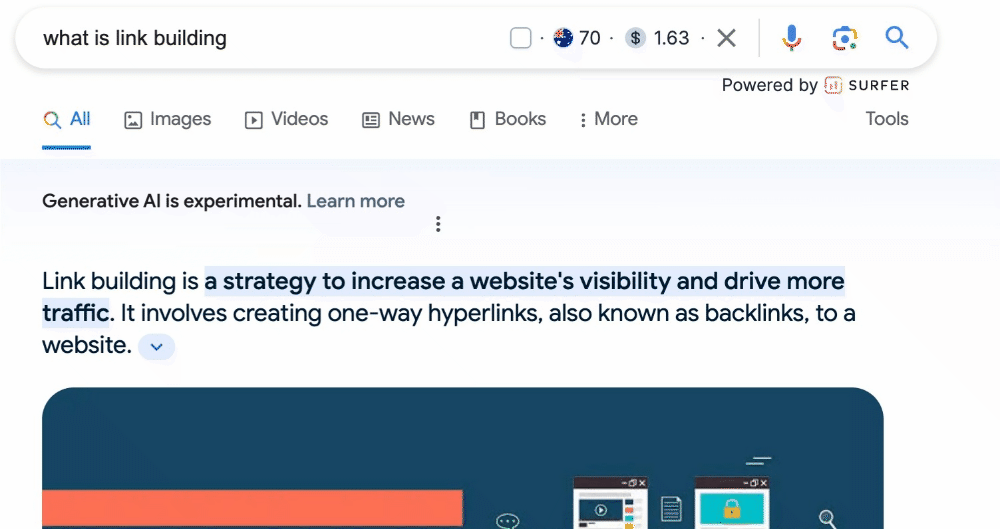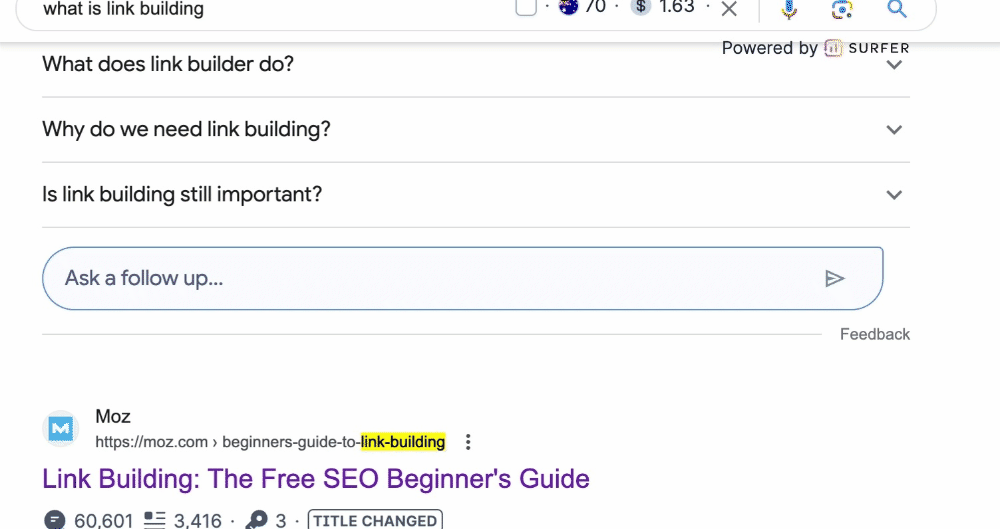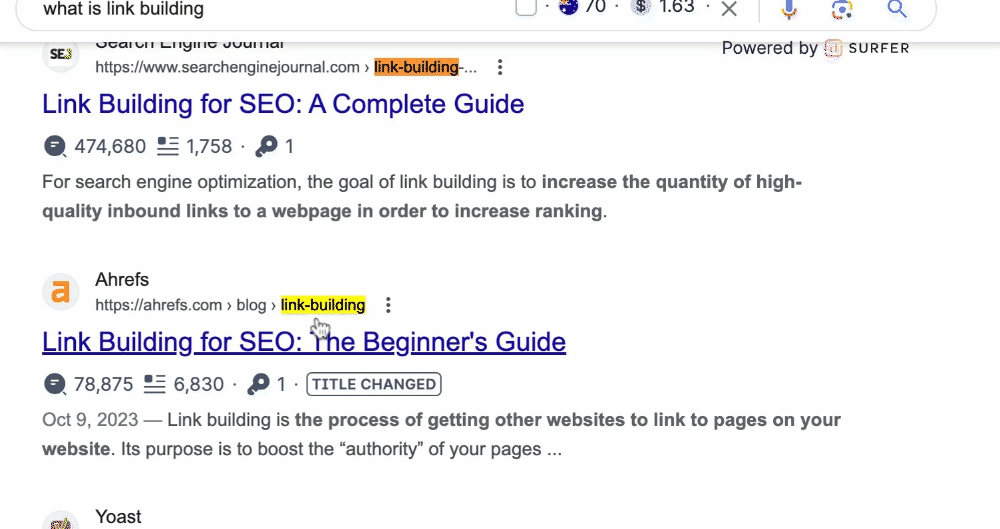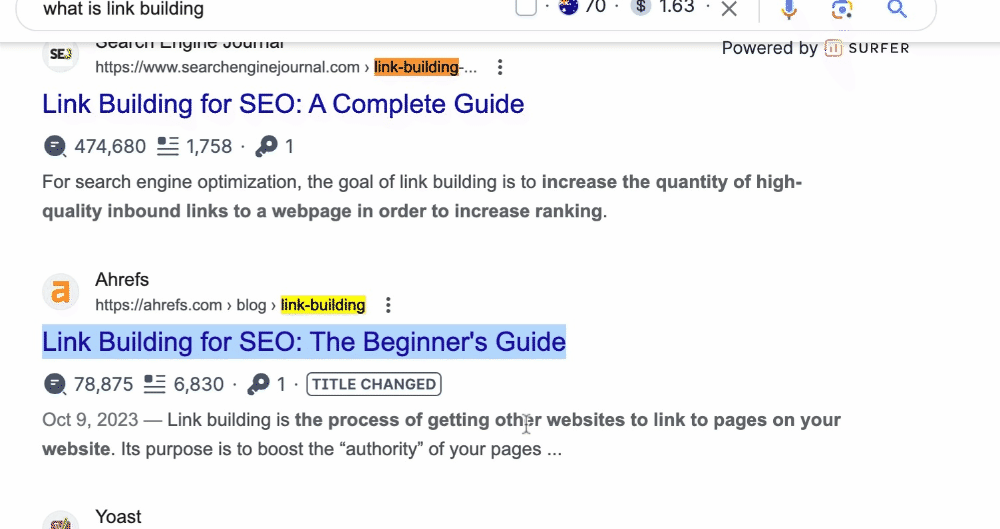
3. Craft Unique and Helpful Content for Users
Your website content should be like a helpful friend.
It needs to be original, offering unique information or solutions that visitors are looking for.
If you’re writing about healthy recipes, make sure your content is not just copied from elsewhere and genuinely helps your visitors learn something new.
Creating optimized, high-quality content involves a few essential practices that ensure your content for search engines is exactly what they’re looking for:
- Natural Keyword Use: Incorporate your keywords into your content in a way that feels natural and readable, avoiding the excessive use of keywords, known as keyword stuffing.
- Match Search Intent: Ensure your content aligns with what users seek when they type in your target keyword.
- Answer the Query Fully: Your content should comprehensively address the user’s query, providing valuable and relevant information.
- Be Straightforward: Answer the user’s question directly within the first 50 words on a page.
- Unique Content: Stand out by offering content that brings something new or different than your competitors.
- Incorporate Visuals: Enhance your pages with visual content like infographics, video content, and podcasts; these types of content make them more engaging and informative.
With the increasing focus on AI being a threat to search engines ranking lower quality content, new concepts such as generative engine optimisation for search features such as the Search Generative Experience are on the rise, meaning here will be a heavy focus on unique and helpful content for the future of SEO.
If you want to learn more about creating Helpful Content, here’s my video guide:
4. Create Smart Title Tags.
Title tags are the names of your web pages in search results.
They’re like book titles that should grab attention and tell readers precisely what the page is about. A reasonable title tag is like saying, “This is exactly what you’re looking for.”
Here are some key tips for crafting effective title tags:
- Short and Sweet: Aim for a length of 50 to 60 characters for your title tags to prevent them from being truncated in search engine results.
- Include Your Target Keyword: Include your target keyword in the title tag. This helps Google and users quickly understand the primary topic of your page.
- Be Unique : Each page on your website should have a distinct title tag. This clarity helps Google differentiate between the pages and makes it straightforward to users what they can expect from each click.
- Make it weird too: Something that a user may not expect to see and grabs the eye as they’re scrolling down the 1st page of search results, giving you an opportunity to increase click-through rate.
5. Write Enticing Meta Descriptions
Meta descriptions are the short summaries under the title tags in search results.
They’re like a movie trailer, giving a sneak peek of what’s on the page and why it’s worth a visit. A well-crafted meta description can convince someone to click on your page.
Here’s how to do it effectively:
- Maintain Optimal Length: Keep your meta description between 140-150 characters. This ensures it fits well in search engine results pages (SERPs) and doesn’t get cut off (truncated)
- Reflect the Page Content Accurately: Your meta description should accurately represent the content on the page. This ensures users get what they expect when they click through, leading to a positive experience and potentially lower bounce rates.
- Place Keywords Naturally and Strategically: Include your primary keyword and brand name early in the meta description. This helps connect the user’s search query and your page. It’s important to ensure relevance to the title tag as well. Then incoperate other semantic keywords naturally into the description.
- Add a Compelling Call-to-Action: End with a strong call-to-action, like “Discover More Here!” to encourage users to click through to your website.
- Ensure Uniqueness: Each meta description should be unique to avoid confusion in the SERPs and make it easier for users to find the specific information they need.
6. Internal Linking Strategy
Internal links are like creating pathways in your website that lead visitors from one page to another.
It helps them find more helpful content and tells search engines how your pages are connected.
For example, a baking blog might link a recipe for apple pie to a page about the best apples for baking.
Internal linking is a crucial aspect of on-page SEO, where you create hyperlinks that lead to other valuable pages within your website.
For example, the term “what is SEO” in the sentence could be linked to a related blog post on your site.
This technique is crucial for several reasons:
- Enhances User Engagement: By linking to other pages on your site, you encourage visitors to explore more content, keeping them engaged for a longer period. This signals to Google that your site is valuable and informative.
- Improves website Crawling: The longer visitors stay and navigate your site, the more time search engines have to crawl and index your pages. This thorough crawling helps Google better understand your website’s content.
- Boosts Page Ranking: Effective internal linking can enhance your website’s SEO, potentially leading to higher rankings in search engine results pages. It allows search engines to discover new pages and understand the context of different content on your site.

7. External Linking Strategy
Think of external linking as building bridges between your website and others.
External links connect your website to valuable information sources on the internet, just like bridges connect and enable transportation between different areas.
This SEO technique is popular for good reasons.
- Providing Additional Information: By linking to external references and resources, you can offer your users more comprehensive information like research papers, case studies, and statistic pages.
- Establish Authority: To gain recognition from Google, experts must prove their expertise and trustworthiness online through platforms like blogs, social media, university profiles, and Amazon author pages. Referencing these experts in your content, particularly for crucial topics (YMYL), via external links is essential for enhancing credibility and aligning with Google’s focus on reliable information.
8. Featured Snippets Sniping
These special boxes appear at the top of Google’s search results, offering a quick answer to a user’s question.
To get your content in these boxes, structure it in a way that directly answers common questions.
For instance, starting a blog post with a clear, concise definition or a list can help.
Here’s how to approach this:
- Research competitors: Use SEO tools like SEMrush or Ahrefs to analyze your competitors’ websites and see if they’re ranking for a featured snippet.
- Create a keyword list: Add keywords that have featured snippets to a list, so you can curate the ones that are relevant to your current blog posts or articles.
- Optimize Your Content: Use H2 and H3 headings to state the keyword question, then give the answer in about 50 words, making your information accessible and easy to navigate for both users and search algorithms.
9. Mobile-Friendly Website
Your website should be like a good book that can be read on any device.
Whether someone uses a phone, tablet, or computer, your site should adjust its layout to give them a good experience.
Google’s emphasis on mobile version optimization significantly impacts search rankings, even for desktop searches.
To ensure your site is optimized for mobile users, it’s essential to focus on several key areas:
- Choose Mobile-Friendly Hosting and Design: Select a website hosting service and a site design or theme that is optimized for mobile performance. This means your website should load quickly and run smoothly on mobile devices.
- Responsive Content Layout: Your website’s content layout should adapt to different screen sizes, ensuring it is easily readable and navigable on smartphones and tablets. This involves a responsive design that automatically adjusts to the user’s device.
- Each time you upload a new page to your website through your CMS, double check how it looks on a mobile, flag any issues for a user experiencing that page.
- Test Your Site’s Mobile Readiness: Need help determining if your site is up to par? Use tools like Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test. This tool allows you to check how well your website performs on mobile devices and provides recommendations for enhancing its performance.
10. Site Speed
A faster website keeps visitors happy and engaged.
Imagine your website is a store, and the speed is how fast the door opens. If it opens slowly, people might leave before they even enter.
Fast page loading is essential for on-page SEO, significantly impacting the user experience and search engine rankings, whether on mobile devices or desktops.
- Google Prioritizes User Experience: Google’s algorithms favor websites that load quickly and smoothly, as they offer a better experience for users. Slow-loading sites have higher bounce rates, as visitors are less likely to wait for the content to load.
- Impact on Conversions and ROI: Site speed isn’t just about user satisfaction; it also affects your website’s conversion rates and return on investment (ROI). Users are likelier to engage with and purchase from sites that provide a fast and seamless experience.
- Use Google’s PageSpeed Insights: Regularly check your website’s loading speed with tools like Google’s PageSpeed Insights. This tool provides the speed score and actionable recommendations to improve your site’s performance.
11. Add Structured Data through Schema Markup
Structured data on your website is like neatly organizing information into a spreadsheet, making it easy for search engines to read and understand.
When you arrange your site’s information this way, you tell search engines precisely what your page contains: a product review, an event, or a recipe.
By incorporating structured data, you effectively label your content, such as prices, opening hours, and product ratings.
This labeling allows search engines to usefully present your content in search results, leading to features like rich snippets:
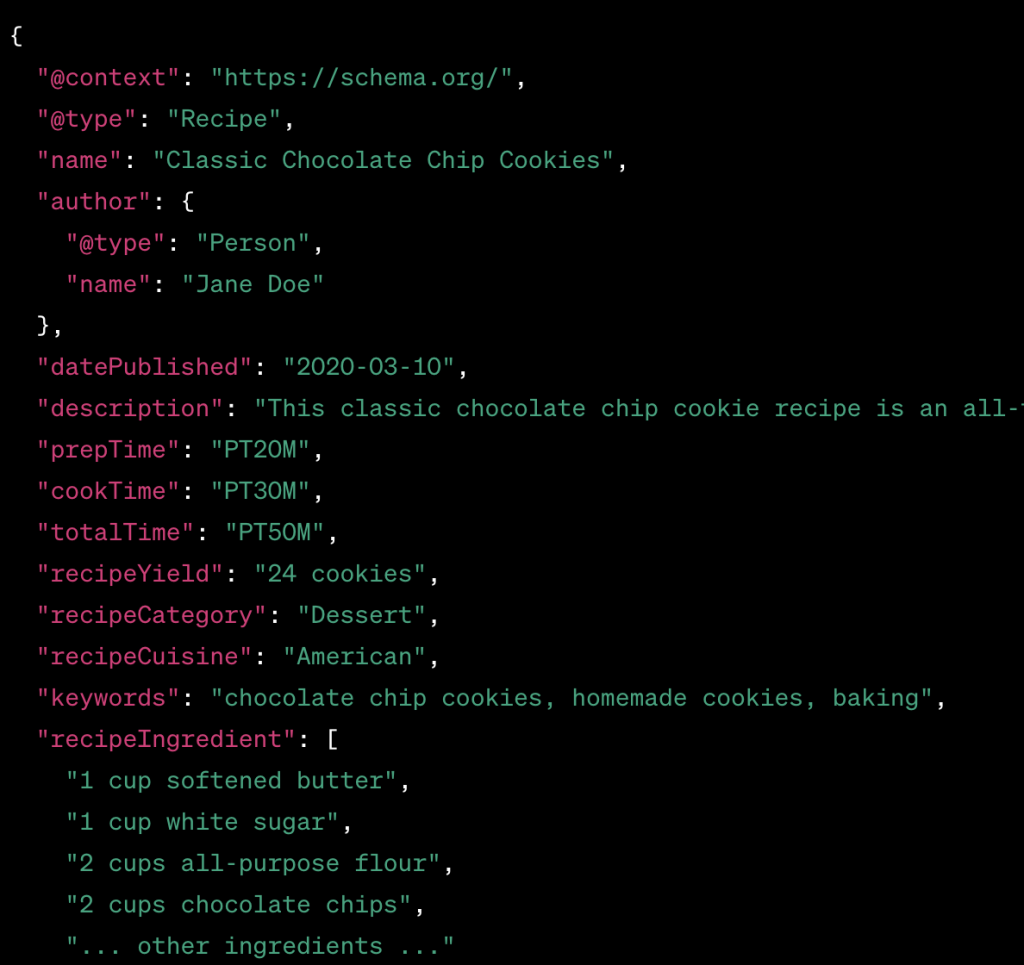
These snippets give users a snapshot of what your page offers, such as star ratings for reviews, even before they click on your site.
Adding Schema markup is the process of applying this structured data.
Think of Schema markup as a guidebook for search engines, a coding language that helps them understand your website’s content and display it attractively in search results.
Using Schema markup, you enhance how search engines interpret and showcase your site, improving visibility and giving users a clearer understanding of your page.
On-Page Optimization Case Study
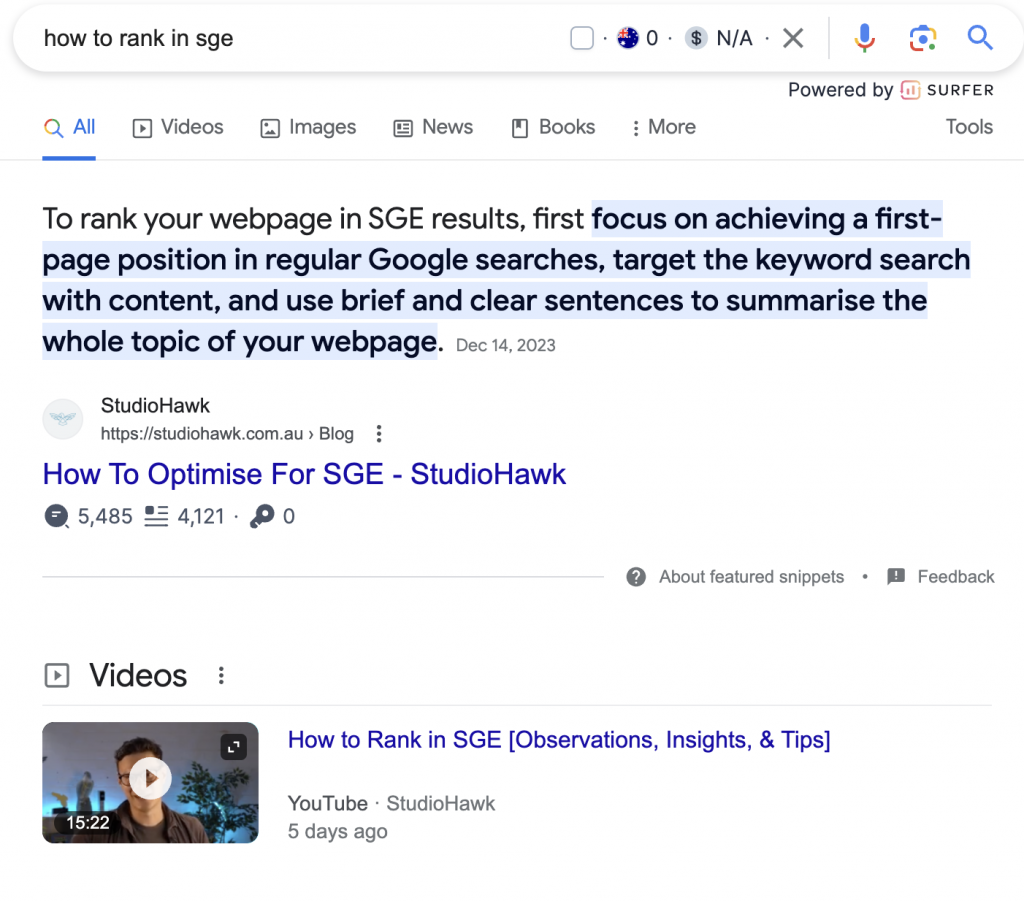
Recently, I’ve been creating content about SGE and saw an opportunity to leverage a low-competition search term, “how to rank in SGE” in preparation for this monumental search shift.
My methodology was as follows:
- Create a content brief through keyword research
- Analyzing the SERP, competitor content, heading structure and content inclusions
- Use a content editor to simplify language to be short, concise, and easy to understand.
- Create video content to support the blog post
- Use ChatGPT to summarize key points
Within 2 weeks, I had captured the featured snippet and its first placement for video results through the YouTube video.
Conclusion
Mastering on-page SEO is crucial for improving your website’s visibility and user engagement.
To optimize your content, use target keywords in your URL, heading, and content.
Creating good content and using smart titles and descriptions will make your on-page SEO stronger.
Internal linking improves site navigation and boosts SEO.
Aim for featured snippets to get your content seen first in search results. Mobile responsiveness and fast site speed are crucial in today’s mobile-first world.
Using structured data with Schema markup improves your site’s appearance in search results.
These elements are essential for optimizing your website and making it valuable to users, driving traffic, and enhancing your online presence.
FAQs
How do you manage large-scale on-page SEO?
For large-scale on-page SEO, start by crawling your site and conducting an SEO audit. Structure your site well and update URLs, titles, and meta descriptions. Focus on tracking relevant keywords and topics for every page. Define clear value propositions and target audiences, and plan engaging page titles. This approach ensures a cohesive, targeted SEO strategy.
What’s the difference between on-page SEO and technical SEO?
On-page SEO focuses on content and format, optimizing elements like titles, keywords, and images for better search relevance. Technical SEO, on the other hand, deals with website code, ensuring it’s clean and efficient for search engine crawling and indexing. Simply put, on-page SEO enhances content visibility, while technical SEO boosts site performance.
When should you do page SEO?
Initiating SEO during web design accelerates results. The initial month typically involves discovery, analysis, strategy, and planning, rather than direct website work. SEO results usually emerge within three to six months, but achieving consistent improvement can take up to a year. Hence, early integration of SEO is crucial for timely effectiveness.
Who should be doing on-page SEO?
On-page SEO is accessible to all, including website owners, bloggers, online marketers, and SEO experts.
Related Guides
These are other guides that are useful in your journey to master on-page SEO:
More Advanced SEO Guide: