The TLDR:
Performance: Prioritize webpage speed, mobile-friendliness, and error-free crawling. Audit for soft 404s and duplicate meta content.
Content: Create unique, engaging SEO-optimized content. Use title tags, meta descriptions, SEO-friendly URLs, and internal links. Apply structured data markup.
Keyword Research: Understand your targeted keyword’s search volume, variations, local searches, competition, and traffic potential.
Link Building / Backlinks / Off-page SEO: List your business in online directories and Google Business Profile. Earn links through quality content and customer referrals.
UI Design: Enhance user engagement with responsive design, F-shaped readability, white space usage, and clear navigation.
Video: Use video sitemaps, snippets in SERPs, transcriptions, and keyword-optimized titles and descriptions.
Call To Action Goal: Focus on one option, consider size, and be descriptive.
YMYL & E-E-A-T: Understand the importance of E-E-A-T quality rating and YMYL.
User Experience: Minimize distractions like intrusive interstitials, excessive popups, auto-playing videos, and slow page load times.
On-Page SEO Checklist – Performance
On-page SEO checklist on performance is a critical aspect of your website. Your website needs to be fast, secure, and have a good user experience to rank better on Google. The following checklist will help ensure that your site has everything it needs to perform at its best.
Analyze web page speed
Analyze your page speed to ensure your site is performing at its best. Speed can be a ranking factor, including user experience, conversion rate, usability, and more.
Page speed is a marketing factor: if your website is slow, you might as well not exist in the eyes of Google. It also affects your brand reputation and competitive advantage because users will assume that if a site loads slowly, it has poor content or functionality on the inside — and leave quickly in search of better options.
Get an overview of the top five issues that affect your site’s speed and how to fix them. Check your page load time against industry benchmarks to know where your site stands.
Test the speed of your site’s mobile pages, including desktop pages.
Find out how well you optimize your site for mobile devices by running a free test with Google’s PageSpeed Insights.
Test robots.txt file
The robots.txt file is a simple text file that helps your site’s search engine crawlers to know which pages they can and can’t access on your website.
It is an essential step toward making sure the content on your site is accessible to users since it prevents any accidental crawling of private information or other sensitive data you should keep secure. Test your robots.txt with the robots.txt Tester.
Make your website more mobile-friendly
Your website must be mobile-friendly if you want to reach a wider audience. Mobile users will avoid sites that are not optimized for their devices.
To ensure this doesn’t happen, ensure your site works on mobile devices and uses responsive design (i.e., a single template that adapts its layout based on the device you use).
Ensure your site loads quickly on smartphones using images no more significant than 600×600 pixels and avoiding plugins that slow download times.
Also, optimize images with file compression software such as ImageOptim or JPEGmini to reduce file sizes without sacrificing quality.
And finally, ensure you’re using a CMS simple enough to manage while still giving you enough control over content display: WordPress has plugins specifically designed for fast loading times on mobile devices.
Drupal offers guidelines for making sites faster, and Joomla has its guide to optimizing pages without losing functionality or aesthetics.
Fix crawl errors in Search Console
The crawl error report helps you find and fix errors Google bot encounters when crawling your website.
Errors in the crawl log include the following:
- Crawling too many URLs at once.
- Not following redirects on a page or site.
- Getting an HTTP 404, 500, or 503 response when requesting a URL.
You can access this report by visiting Search Console > Crawl > Crawl statistics. Then click on Crawl errors.
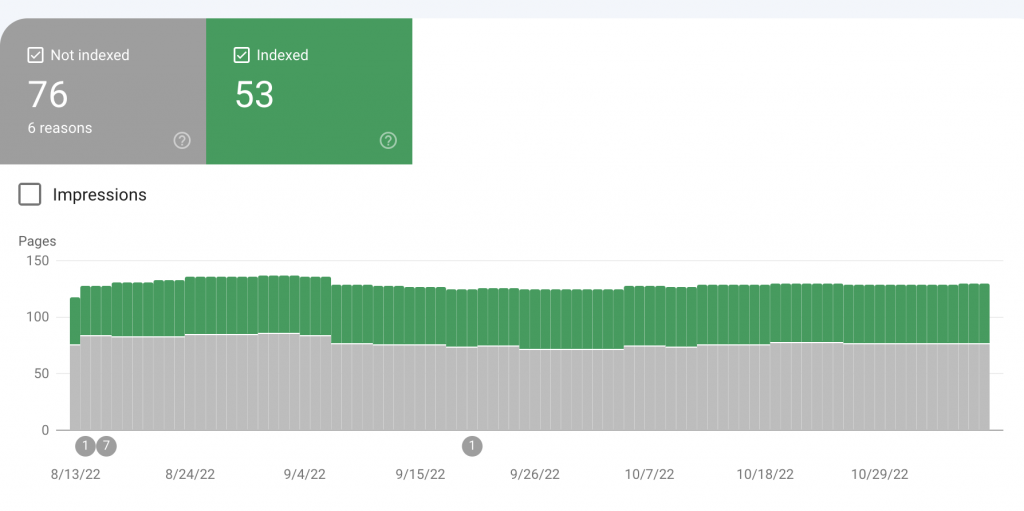
The table will show you how many pages Google bot blocked because of these issues, plus it has more details about each error type so you can determine which ones are most important to fix first.
When there is an error on a page, the Google bot will indicate a problem with the URL by shading it green. Not-indexed pages are in grey and error pages are in red.
In addition to fixing these problems directly in Search Console, you can take other steps for the Google bot to crawl the site.
Audit pages with soft 404s
What is a soft 404?
A soft 404 is an HTTP response code that means a Page is not found but usually isn’t a correct 404 error.
It can happen when Google’s search algorithm has moved or deleted the page you’re trying to access but didn’t mark it as permanently removed from its index.
You can also trigger a soft 404 if you type in a URL or keyword you know exists on your site but doesn’t include the exact structure of your URL.
These situations result in broken links because they appear like regular pages with content, but they’re technically inaccessible due to their status as soft 404s.
If you leave them alone, these errors will likely cause people who click on those links — logged-in users included — to bounce back immediately and get frustrated with your website’s usability.
Look for duplicate meta content.
There is a possibility of duplicate meta content if you have a website but haven’t done much SEO.
If this is the case, it’s time to take action: duplicate meta content can cause problems for search engines and users.
First off, what exactly is duplicate meta content?
It refers to a situation where two or more pages of your site contain similar (or identical) information about their titles or descriptions.
Search engines are not fond of this type of thing — they want unique content to understand what each page is about — and they tend to punish websites with too much-duplicated information by lowering their rankings on search results pages (SERPs).
In addition, if you have multiple versions of the same page within an internal linking structure (this means numerous links pointing back at a particular page), Google may choose not to index those pages as part of its crawlable index.
Instead, it will only index one version per URL and ignore any others since nothing differentiates them from each other.
Run an audit to check broken internal links (404 pages)
Use a broken link checker to find internal links with 404 response codes.
If you’re using a tool like Screaming Frog or Broken Link Checker, you can run it against your site and find all the broken links on your website.
Upgrade plugins and themes
Ensure your plugins and themes are up to date. If you’ve been using a plugin for several years, there’s no need to continue using an outdated version.
Updating all plugins ensures they don’t contain bugs or vulnerabilities that affect your site’s overall performance.
The same applies to themes; if one isn’t performing as expected, check its settings before upgrading anything else.
Inline CSS
Use inline CSS where possible to improve page performance. Inline CSS is easy to maintain and secure since you can write the styles in the source code of your website.
External stylesheets can be hard to update, so you should use them only when you need cross-browser support or want your CSS files to be downloaded independently.
Check image ALT tags.
Alternative text (Alt tags) is a crucial part of SEO performance. They provide context for screen readers and help Google understand what an image is about.
They should be unique to each page on which they appear and individual to each image (i.e., don’t reuse alt tags).
While at it, ensure that your title tag is descriptive and includes keywords.
On Page SEO Checklist – Content
The SEO checklist will help you ensure that all the pieces of your page — title tag, meta description, URL, headings, and more — are working together to increase your chances of appearing in search results.
Content-based SEO is about creating engaging, high-quality content that resonates with users.
Optimize page title tags
- The title tag is the first element to appear on your search engine results page (SERP).
- A good title is relevant, descriptive, and unique to each page so that it accurately represents what a user would expect to see when they arrive at your website.
- Keep your titles short — 60 characters or fewer— because Google truncates long titles by default.
Page titles, also known as title tags, play a pivotal role in SEO strategy. They are the first point of contact between your website and potential visitors browsing the search engine results pages (SERPs). A well-optimized title tag can significantly influence click-through rates, making it an essential element in driving organic traffic to your site. However, optimizing title tags isn’t just about improving rankings; it’s also about providing context and relevance to your audience and search engines.
The importance of title tags cannot be overstated. They serve as an initial cue to the topical subject matter of the page, appearing prominently on SERPs and in the browser window. However, on its own, the title tag has little impact on organic rankings. It’s the combination of a well-crafted title tag with other on-page elements that builds important context and subject-matter relevance for a page. For instance, a title tag is most impactful when it introduces the topic of the page and the same important keywords are used in body copy, image alt attribute, the meta description, URL, and other aspects of the page.
When it comes to optimizing title tags, there are several key aspects to consider. First, understand the page’s context within the site. The title tag for a homepage will be different from that of a blog post or product page. Second, consider the searcher’s intent and use relevant keywords that your audience is using in their searches. Third, ensure topical relevance within the page. The words used in the title tag should also be used in other parts of the page to tie the topic together.
Let’s consider some examples. A good title tag could be “5-Piece Customized BBQ Utensil Set by The Man Registry.” It’s specific, relevant, and includes important keywords. On the other hand, a title tag like “Product Page” is vague and doesn’t provide any context or relevance, making it a poor choice.
Remember, the goal of a title tag is not just to include keywords but to provide a concise, accurate representation of the page’s content. It’s about balancing SEO best practices with providing a meaningful, compelling reason for users to click on your link in the SERPs.
Meta Description Optimization: Crafting Compelling Summaries
- The meta description is the first thing people read when they see a search result in their browser. It’s essential to ensure it is unique and compelling so that users click on your page instead of another.
- Meta descriptions should be between 150 and 160 characters long, though some search engines may allow longer descriptions.
- Write them naturally, not with keywords stuffed into the text. You don’t want to look like you’re trying too hard.
Meta descriptions, while not a direct ranking factor, play a significant role in attracting clicks from search engine results pages (SERPs). These HTML elements provide a summary of your webpage’s content, giving potential visitors a snapshot of what to expect before they click through. An effective meta description can significantly increase your click-through rate, driving more organic traffic to your site.
When writing a meta description, it’s important to keep a few key principles in mind. First, it should accurately summarize the content of the webpage. Google and other search engines use meta descriptions to understand the context of your page, and they may choose to display your meta description in the SERPs if it provides a more accurate description than the on-page content. However, if the meta description is not accurate, Google may rewrite it, using text from the visible part of the webpage instead.
Second, your meta description should include relevant keywords. While Google states that they don’t use keywords in the meta description for ranking purposes, these keywords are often highlighted in the SERPs, drawing the reader’s attention and potentially increasing the likelihood of a click.
Third, your meta description should be compelling. Think of it as a pitch to convince the user that your page is exactly what they’re looking for. It should inspire confidence in the user that your webpage contains the information they’re seeking.
For example, a good meta description for a personal injury attorney’s blog post might be: “Pain and suffering are very real to the victim in a personal injury case. Learn more about how to reduce discomfort from our personal injury attorneys in this latest blog post.” This description accurately summarizes the content of the page, includes relevant keywords, and provides a compelling reason for the user to click through.
Remember, the goal of a meta description is not just to include keywords, but to provide a concise, accurate, and compelling summary of your page’s content. It’s about balancing SEO best practices with providing a meaningful, compelling reason for users to click on your link in the SERPs.
Create an SEO-friendly URL
Ensure your URL is short and easy to remember. Once you’ve chosen a domain name, stick with it so that people can easily find your site.
Don’t use underscores or hyphens in URLs. These characters are unnecessary and will make the URL harder to read, especially when they are part of the keyword you want people to type into their browser bar to get to your site (e.g., http://www.example-company-name.com/products/product1).
Avoid special characters such as ampersands (&), non-alphanumeric characters such as äöü߀$%&'()*, spaces, or dashes (-).
Special characters may cause problems when users try to type them into their web browsers, or search engines will not recognize them as valid words.
Image Optimization and Alt Text: Enhancing SEO and Accessibility
Images are a crucial part of a website’s content, not just for the visual appeal but also for SEO. Properly optimized images can improve your site’s performance, enhance user experience, and provide additional ranking opportunities in search engines. One of the key aspects of image optimization is the use of alt text, also known as “alt descriptions” or “alt tags.”
Alt text is a written description that is displayed in place of an image on a webpage if the image fails to load on a user’s screen. This serves two important functions. First, it helps screen-reading tools describe images to visually impaired readers, making your website more accessible. Second, it allows search engines to better understand the image content, which can improve your website’s SEO.
When writing alt text, it’s important to be descriptive and specific, accurately conveying the content and purpose of the image. For example, instead of using a generic description like “dog,” a more effective alt text would be “a golden retriever playing fetch in a park.” This provides a much clearer picture of what the image is about.
In addition, it’s beneficial to include relevant keywords in your alt text. This can help your images show up in image search results, potentially driving more traffic to your site. However, avoid keyword stuffing as it can lead to a poor user experience and may be penalized by search engines.
Remember, while alt text is important for SEO, the primary purpose is to describe images to those who cannot see them. Always prioritize creating meaningful descriptions that improve accessibility and user experience.
Add internal links
Internal links are the links that lead you from one page of a website to another. They’re crucial because they help guide visitors around the site and can improve user experience, SEO, and page load speed.
Here’s an example: If you were looking for information about puppies on a website, an internal link could take you to another page on that same site with more information about puppy care.
You want to ensure at least three-six internal links per page or landing page so that people who visit your site can easily navigate it without relying solely on search engines for navigation guidance, with the correct anchor text to add relevance to the page.
Markup content with structured data
It is a way of adding metadata to your web pages so that search engines can better understand the content.
You can use it on both desktop and mobile sites, and it can tell Google what the page is about, who wrote it, whether it contains images or videos, and much more.
Structured data markup uses HTML tags in the code of your page’s HTML page files specially designed for this purpose.
You can think of structured data as similar to meta tags — it adds meaning to content by identifying different information within a page (e.g., author name).
The goal is to improve how search engines interpret web pages and present them in search results.
Structured data allows you to specify things like:
- Author name.
- Date published.
- Article type (e.g., news article).
- Category/topic (e.g., sports).
- Headings and numbered lists
Headings and numbered lists are tools to use in your written content to help readers understand how to organize the information.
Headings help organize the content by providing visual cues.
For example, if you have a section about Types of CSS, headings like Classes and IDs would be good choices for organizing that section.
It helps readers find information quickly when scanning your page for topics or types of information.
Numbered lists are also effective at helping readers navigate through large amounts of text because they provide a visual hierarchy for where certain pieces fit within larger chunks of text:
- Headings highlight key points.
- Subheadings highlight subpoints under a more extensive idea (e.g., subheadings under an article title).
- Numbered lists further divide them into smaller parts.
Ensure your content is unique and engaging
Use short sentences. The average length of a sentence should not be longer than 15 words.
Use simple words. Instead of using complicated language in your content, use everyday language that everyone understands — and avoid jargon at all costs.
Use active voice instead of passive voice. Passive voice makes sentences sound vague and indirect — it doesn’t clarify who did what action or why it happened, whereas active voice explains who did what action and why it happened.
Use lists when possible: they make information easier to read. If you’re listing items one after another, consider putting each item on its line (you can use bullets). It will also help break up long chunks of text into smaller bits that are easier for people to digest quickly.
It is especially true if those chunks get long (say over 200 words). Readers may lose focus because their eyes have trouble skimming large blocks without skipping over important details.
Is creating a unique content king?
Creating unique content for on-page can help you get more traffic, and it’s also a good idea because it helps with your rankings.
When you write unique content, you are giving your readers something they can’t find anywhere else — and can keep them coming back to your site.
When Google indexes your site, it also pulls in the links to other pages on the Internet that reference your content. You increase the chances that Google will pick up on those links and include them in its ranking algorithm.
It means that when someone searches for something related to what you wrote about, they’ll be able to find your page before others.
The Role of Helpful Content in SEO
Helpful content is now a crucial factor in SEO, as Google’s algorithms are increasingly prioritizing websites that provide high-quality, useful information. This is part of Google’s “Helpful Content Update”, which uses machine learning to predict whether content is likely to be the most helpful for a searcher. If a website’s content consistently falls short of these expectations, it may be classified as having ‘unhelpful content’, which can negatively impact its visibility on Google’s search results.
The importance of helpful content in SEO is further emphasized by Google’s use of AI systems in their ranking algorithms. These systems, such as the Search Generative Experience (SGE) and Google’s Bard AI chat technology, are reshaping the way we search for information online. They are designed to present the searcher with pages that are likely to be helpful and satisfy their search intent.
Optimizing for Helpful Content
To optimize for helpful content, it’s essential to align with Google’s criteria for quality as laid out in their Quality Rater’s Guidelines. These guidelines provide a comprehensive overview of what Google considers to be high-quality content. They include questions like, “Does this article contain insightful analysis or interesting information that is beyond obvious?” and “Does the page provide substantial value when compared to other pages in search results?”
In addition to following these guidelines, it’s also important to keep up with the latest developments in Google’s AI systems. Understanding how these systems work can provide valuable insights into how to create content that aligns with what they are designed to reward.
In conclusion, the importance of helpful content in SEO cannot be overstated. By creating high-quality, valuable content that aligns with Google’s guidelines and understanding the role of AI in search, website owners can improve their visibility on Google and provide a better experience for their users.
Use keywords appropriately
The first step in optimizing your on-page SEO is to include the primary keyword in your title tag. Use your keyword phrase in the title and at least one subheading on the page.
Ensure your primary keyword(s) are in at least one subheading on the page (an H2, H3, etc.).
It is especially crucial for longer content, as it helps Google understand what is essential about each section of text within that article.
Place your keyword within the first 100 words of your content.
Check keyword density
When writing your on-page SEO content, use the keyword density checker to ensure that your article has an appropriate number of keywords.
For example, if you are writing a piece on how to sell used books online, mention the word book at least once every 200 words.
If not, your keyword density is too low, and Google won’t know what information it needs to display in its search results for users looking for information about selling second-hand books online.
You can also use tools to determine how many keywords appear in your article and whether it is too high or too low.
Ensure your internal links work
Internal links are a great way to show search engines that your content is relevant and can help visitors navigate your site efficiently. Internal linking is a crucial part of the on-page SEO checklist.
To create internal links, understand the types of pages you want to link.
For example:
If you’re writing about a specific product or service, there should be a separate page for each one with its URL (example: https://www.examplecompany.com/product-name/).
On this page, describe the product or service in detail and link back to your home page at least once, so people know how they arrived at that page.
It will also help search engines find these pages easily in their algorithms.
On Page SEO Checklist — Keyword Research
Keyword research is one of the most crucial steps in on page SEO, but it can be hard to know where to start.
This on-page SEO checklist will guide you through some of the best practices for keyword research, including how to measure your results and what questions you should ask yourself as you build your list.
Any search volume for your targeted keyword?
Search volume is an essential factor in SEO. It is the number of searches for a keyword on Google.
It’s a good indicator of keyword competition and how much traffic you can get from that particular keyword.
For example, if the average monthly search volume for a keyword is 10k per month, your site will get approximately 1% (10k divided by 100) of those searches if you rank #1 on Google.
What are exact, phrase, and broad search volumes?
There is a big difference between exact, phrase, and broad search volumes. The exact search volume is the most accurate because it counts only searches that include the exact keyword.
Phrase search volume includes searches that include all words in your keyword.
Broad will include any variation of your keywords so long as they are close enough to relate.
How many local searches do you get for this keyword?
In addition to looking at the search volume, it’s essential to determine how many local searches people are performing for your keyword.
It will help you determine whether it’s worth investing in a local campaign for this keyword. A local search is any search that includes the city, state, or zip code in the query.
Local searches are more prevalent in smaller cities than in larger ones because of the distance between people.
However, there are still plenty of large cities where consumers may want to find products and services near them, so don’t rule out a keyword with high local search volume just because its location isn’t what you expected.
Why compare the targeted keyword to other keywords?
While some marketers focus on a single keyword for their campaign, it isn’t always wise. Most SEO professionals recommend that you create a list of five or more relevant keywords for each campaign.
It will help maximize the potential reach and impact of your campaign. Ensuring you have enough coverage across broad searches, long-tail searches (keywords with three or more words), and local searches (geographically-specific terms).
If you focus on just one keyword, ensure it is highly relevant globally and locally.
Does your targeted keyword have any apparent substitutes?
If a keyword has apparent substitutes, it’s probably not a good idea to target that keyword.
For example, targeting the keyword [optical frames] and its direct substitute is [frames]. It’s unlikely that people searching for one would be satisfied with the results of the other.
What is the traffic potential for your targeted keyword?
At this point, you should have a list of keywords relevant to your business. The next step is to check the traffic potential for these keywords based on the first page of search results. It will help you determine which ones are worth pursuing.
You can do this by searching for your keyword and looking at the top 10 results for:
- That keyword.
- A related keyword (or two).
- A related keyword or two in the same space.
- What is the competition for your targeted keyword?
It’s essential to understand how to measure competition to start. The number of pages currently ranking for a keyword is a way to measure competition.
For example, the quality and authority of these pages also contribute to your content’s ability to rank.
Is there room on the first page to get ranked?
The first step is to find the top 10 URLs ranking on page one.
There are many tools available to do this. They give you an overall SEO score for each URL and help you determine whether a keyword is worth targeting.
If there’s good competition for a keyword, you’ll want to look for another with less competition (higher search volume).
If there’s no room on the first page for your website, try using long-tail keywords instead of broad ones, as they tend to have less competition because they’re more specific and targeted toward a smaller audience.
How many long-tail keywords?
Long tail keywords are usually more targeted and specific. They tend to have low search volume and are not typical of keyword research, but they can be helpful when targeting specific audiences.
As you move down the results list and choose words that describe the audience you want, you may notice that some phrases are not very popular in Google’s SERPs (search engine results pages).
It indicates a few people use these phrases when searching for what you offer or need.
Instead of using these less popular phrases in your content marketing strategy, focus on using other combinations of words with high search volumes and higher relevance ratings from Google’s algorithm because humans and machines consider them essential.
On Page SEO Checklist – Link Building / Backlinks / Off-page SEO
Link building is creating links to your website from other websites. People used to build it through no follow links, but now social media sites are starting to become a popular way to create links.
List your business in online directories.
List your business in online directories. While you may think of online directories only for local businesses, that’s not always the case. Many guides cater to particular industries or niches and can be a great way to build links and boost rankings.
Get listed on Google My Business. It is time to start if you don’t have your business listed on Google My Business. It will help people find you when they search locally on Google.
Create a Google Business Profile
Creating a Google Business Profile is an essential first step for any local business looking to gain more visibility online. GMB pages are crucial for search engine optimization, as they give you the opportunity to:
- Show up in search results when people look for your business (which means more leads).
- Get verified by Google and appear on their Local Pack of businesses at the top of the SERPs (search engine results pages) in their respective geographic area.
- Add rich snippets to your site that provide additional information like hours of operation, price range, etc., which improves user experience and increases click-through rates (which means even more leads).
Optimize your website for local search
Using local keywords in your:
- Content.
- Meta description.
- Title tag.
- URL (including the file name).
- Alt text for images on the page.
- H1-H6 tags.
Claim your Yelp listing
Claiming your Yelp listing is a great way to start building links. Your listing will be visible across the site and can help you attract new customers and increase customer loyalty.
Yelp is a local directory that helps users find businesses in their area through reviews, recommendations, photos, and more.
Earn links by creating content others want to share
- Create content that is useful, interesting, and entertaining.
- Ensure the content is relevant to your target audience.
- Make it easy for others to share your content by adding share buttons at the top of each page.
- Ensure the content is well-written and easy to understand.
Include Outbound links
The number of outbound links you have that point to your site signals search engines that you are an authoritative site on your topic.
When a user searches for information about your topic, Google will see that many people have linked to your site when researching this topic and rank it accordingly.
The most important thing to remember about outbound links is they should be relevant to the topic at hand — if you’re writing about cars, don’t link to an article about cats.
Understand that your reader is looking for information on a specific topic, so ensure you’re linking to relevant sites.
Another thing to consider when creating outbound links is that it’s best not to overdo it — if you have too many outbound links on your page, it could look spammy and hurt your SEO efforts instead of helping them.
Ask happy customers to link to you.
Asking happy customers to link to you is an easy way to get third-party links and improve your rankings.
These links can help build trust with prospective customers who look at your company’s website when researching a purchase.
To get started, encourage your happy customers who requested a quote or service from you if they would be willing to put a link on their site back to yours.
You can also find out if they would be interested in writing a testimonial for your business and then adding it as an additional link on their website or blog.
On-page link building can be a powerful tool when you do it right. It’s crucial to consider this as an ongoing process, though. You won’t get all the links you need overnight — it takes time.
On Page SEO Checklist – User Interface (UI) Design
The user interface design of an online page is the layout and formatting of the content and functionality on that page. It includes visual design cues like color, font size, and how to use the different elements of a site’s interface to help users find information quickly and easily.
Better user engagement
An engaging user interface will help you build trust and credibility with your audience.
Responsive web design
Responsive web design technique ensures designs appear correctly on any device, from desktop to mobile phone.
The responsive web design aims to create websites that provide an optimal experience — easy reading and minimum navigation resizing, panning, and scrolling — across devices (from desktop computer monitors to mobile phones).
It helps ensure your web content will look great no matter what device you’re using or what application you’re running.
F-shaped pattern readability
A better way to determine whether your page is readable is by looking at the F-shaped pattern.
The f-shaped pattern isn’t just something you see when someone has fallen asleep reading their phone — it’s a reading pattern that most people follow when they read a page.
The eyes move from the top left corner of the page downward toward the bottom right corner. Then they move back up again before returning to where they started.
Visitors won’t have time to reach your content before moving on if your design doesn’t catch their attention quickly enough.
White space between paragraphs
With white space, the best rule of thumb is — the more, the merrier. There are plenty of reasons why white space is crucial for readability and SEO.
White space makes your content easier to read. It removes distractions from the page and allows users to focus on what matters most — the words you want them to see.
White space improves search engine rankings boosting keyword density and making pages appear less cluttered than those with dense formatting.
It also helps visitors find what they’re looking for faster because there aren’t as many barriers between headings, paragraphs, images, and other elements on the page.
Navigation that is easy to follow
Here are some guidelines for ensuring your users can easily find where they’re going and get there in the most efficient way possible:
Navigation should be clear and straightforward. It should be easy to understand at first glance so that people don’t have to stop and think about where they should go next or what kind of content is on each page.
It means avoiding much text (and incredibly long text) in navigation labels; using icons instead can help make things more visual and intuitive.
Navigation should be consistent throughout the site. Ensure all sections have similar layouts so users know what they can expect when they reach them.
For example, if some pages only have one main navigation bar while others have multiple levels of menus below it, this could cause confusion among visitors.
Many studies show that well-designed websites get better rankings than those poorly designed but stuffed full of keywords and links.
On Page SEO Checklist — Video
Set up a video sitemap
A video sitemap is an XML file that lists the URLs of all your videos, along with other information like title, thumbnail, and description.
Google indexes new pages faster if you include them in the search engine’s index. Listing your videos on a single page makes it easier for a Google bot to crawl them at once.
You should submit your sitemap to search engines every time you add or change a video, but if you offer all these URLs manually every time you tweak (like changing metadata), it can be very time-consuming.
Use video snippets in SERPs.
Video snippets are a new feature that many major search engines, including Google, Bing, and Yahoo!, have rolled out.
These snippets are generated from the first few seconds of your video and displayed on SERPs as a preview.
You can use this snippet to get more clicks and views on your videos to improve your rankings.
The main benefit of video snippets is that they tell users what to watch before they even click through to your page. It leads to higher click-through rates.
Create video transcriptions
Transcripts are a must for on-page and help search engines understand the content of your videos.
They also help users understand the content of your videos and can help you rank for keywords in your video’s title and description.
Optimize video titles and descriptions
The title and description are essential elements of your video. They should be short and catchy, include a call to action, and include keywords related to your business to maximize SEO potential.
The title should include Your business or product name. It is more important if you have multiple videos about different topics or products that people can’t easily distinguish through the thumbnail image.
For example, if you have an auto repair shop named ABC Auto Care Center, it’s probably not enough to list ABC Auto Care Center as your video title. Instead, recording something like ABC Auto Care Center | Your Local Transmission Experts would be better.
Your location. You may want all viewers who search for transmission services near their location or within 100 miles (ca. 161 km) to see this video first over others by other companies or competitors nearby.
It will help identify which service provider they want working on their car before calling them for an appointment.
Add closed captioning
Google gives you bonus points when you provide closed captioning on your video.
It makes it more accessible for those with hearing impairment because YouTube’s algorithms recognize the presence or absence of closed captioning.
It is a signal that indicates whether a video will be relevant to people searching for it.
Closed captioning is excellent for on-page. Your videos need to be searchable by keywords if they’re going to show up on searches.
Captions are an excellent way of adding additional metadata (words about words) to help improve your rankings in Google Search.
Closed captioning for user experience. Providing captions on all your videos also improves the user experience.
It means that viewers don’t have to listen over to understand what’s going on in each scene: instead, they can read along at their own pace while relaxing comfortably from start to finish.
Add relevant keywords to video tags and titles.
For your videos, it’s crucial to add the exact keywords that you would use in text content.
Also, use the same keyword density as you would for text content so that Google knows which words and phrases are most important.
When possible, include variations of those keywords.
Finally, ensure your video tags and titles reflect the intent of the users searching for this type of information — which will help Google determine how well your video matches up with their search query.
Get links from local businesses for your videos.
It will help you get better rankings in Google Places. Also, it will drive more traffic back to your website.
Ensure the business is relevant and related to the video’s content, keywords and topic.
Remember that a video is only as good as its title, description, and tags. Therefore, be sure to pay attention when writing those sections.
On Page SEO Checklist – Call To Action Goal
The main goal of the call to action (CTA) is to increase leads and sales using a clear call to action.
It tracks what happens when users click a CTA. It’s best to follow your conversion funnel and understand if your CTAs are working well.
If you don’t know how much revenue you make from each click, it’s impossible to tell whether your CTAs are effective. The only way to do that is by using a CTA goal inside Google Analytics (GA).
Narrow down your focus
When creating CTA goals, you should be laser-focused on one goal and action. It might sound counterintuitive. After all, it’s about attracting new customers.
But if your marketing team is spreading itself too thin, trying to hit multiple objectives, you may miss out on crucial opportunities.
Size matters
Choose the right size for your CTA. To be effective, CTAs should stand out from other elements on a web page, and visitors can easily see them.
Using too small or too large a CTA will negatively impact its success and conversion rate.
The recommended size is between 24×24 pixels and 48×48 pixels (however, you can test variations of this range to see what works best).
Size matters because it affects the success of your CTA. If people don’t notice your call-to-action button, they won’t click it — which means they won’t convert into leads or sales.
Give only one option.
It is an exercise in simplicity and efficiency. The goal is to give your users no choice but to convert, so you should offer them only one way.
If there are multiple ways users can do something or buy something, they will be confused about which method works best for them.
You run the risk of losing their attention or interest altogether.
Be descriptive
A CTA goal should be brief, descriptive, and to the point. It should tell people exactly what action you want them to take next and how it fits into their overall goal. Here’s the breakdown of what this means:
Action. Describe the action users should take. It could be simple: buy now, sign up, or check out my website.
Results. Describe the impact of the action. Say you sell sunglasses — your CTA might say something like getting $20 off your next order when you buy today! It tells people what they can expect if they click through.
Benefits. Explain why this action is beneficial (and don’t forget about longer-term benefits).
If someone buys a product from your e-commerce store after clicking through from an email campaign, ensure you explain how easy it is to return or exchange items.
It helps increase customer satisfaction and keeps them coming back for more purchases.
If a user signs up for an account on your website, let them know there will be discounts available only for members in future emails.
It ensures they know that signing up is worth their time investment.
The more specific you can be with your CTAs, the better your conversion rate will be because users know what they’ll get when they click them.
On Page SEO Checklist — YMYL & E-E-A-T
E-E-A-T quality rating
E-E-A-T stands for experience, expertise, authority, and trustworthiness.
It is a quality rating system that combines three factors:
- Experience (E) the experience a content writer have in any subject.
- Expertise (E). The level of knowledge, education, have in any subject.
- Authoritativeness (A). How authoritative a site or piece of content is to its audience. You can measure it by the number of backlinks and the reputation of those who link to it.
- Trustworthiness (T). It refers to how trustworthy or reliable you think a particular piece of information depends on your opinion about its author’s expertise, knowledge base, and credibility.
You can think of each of these things as a piece that makes up your overall credit score. The more expert you are in your field, the higher your expertise score will be.
When you cite authoritative sources on your website and social media accounts, the higher your authority score will be
The more trusted content you publish (and share), your trustworthiness score will be higher. All three components combine to form an overall credibility score that Google uses to rank pages on its results pages (SERPs).
YMYL — Your Money or Your Life
YMYL stands for Your Money or Your Life. It’s a term used by Search Engines to denote sites that have a high level of trust, authority, and expertise.
It refers to content directly impacting the reader’s finances, health, safety, and well-being. A good example would be a mortgage broker who publishes pages on their website about what kind of house you should buy or how much money you need to save up for the down payment.
YMYL is essential because Google has stated that they want people searching online to get high-quality information when they type something into the search bar of their browser window.
They also ensure users don’t fall victim to scams or fraud when looking for solutions online.
For example, if your website provides answers about health conditions without medical training, it could negatively impact your site’s ranking on SERPs.
Why is YMYL important?
The goal of any website is to provide valuable resources for users to make informed decisions about their lives.
Whether it’s buying products or services, getting advice about disease prevention and treatment options, etc., all while providing high-quality information for users.
On-Page SEO Checklist – User Experience
UX, or user experience, is the holistic approach to ensuring users have a good experience when interacting with your product.
User experience is about ensuring that visitors can easily find what they’re looking for and how easy or difficult it is to use your website or app.
It’s easy to understand why this is important: customers won’t stay if they don’t enjoy using your product. But what is a good experience? Well, some things can negatively impact UX and make it less than stellar for users.
Do not distract with intrusive interstitials.
You’ve been here before: you land on a website, and a box pops up asking you to subscribe or asking for your email address to view the content. It is an intrusive interstitial and increasingly common phenomenon on the web.
It can be annoying when these popups get in your way while you are trying to read something. They can make it hard to find the content you want.
Too many popups?
Popups are not suitable for the user experience. A popup that asks you to subscribe or sign up for something is another, but a popup that crashes your browser or forces you to download software is another. Popups can also be a distraction from what you’re doing.
Too many popups are also nasty for security because they increase the risk of identity theft by forcing users into making quick decisions about whether they want information from unverified sources.
They take away from the user experience by being intrusive and distracting.
Some users may not use services altogether because they don’t want to compromise their personal information.
Do not use auto-playing videos.
Auto-playing videos are a significant annoyance, and there’s more than one way to combat them.
In Chrome, you can turn off auto-playing videos in your browser settings under Privacy and click Content settings.
You can also install extensions that stop YouTube from playing videos automatically.
For Firefox users, you can use an extension that stops most auto-playing videos from playing on your computer (including YouTube videos).
Avoid slow page load times.
Pages that take too long to load are highly annoying for users, especially on mobile devices. These factors affect your page speed: server response time, network latency, and browser rendering time.
- Server response time. It is how long it takes for your server to send data back to the browser once a visitor has requested it or user action (like clicking on a link).
- Network latency. The amount of time it takes for data packets to travel between two locations over a network connection (such as an Internet connection).
- Browser rendering time. The amount of time a web browser spends rendering elements like images or scripts.
UX is a big deal, and it’s crucial to ensure your website or app doesn’t get in the way of users doing what they want. If your product has poor UX, people will be frustrated and leave. It may not seem like much, but small changes can make a big difference in how people perceive your site.
Conclusion
This SEO checklist has given you a few things to consider in your on-page SEO. It’s not exhaustive, but it’s an excellent place to start. Remember that the key to SEO isn’t just writing great content; it’s also making it easy for Google and users to read and understand. Take these on-page SEO checklist tips into account as you write your next piece, and keep experimenting with different approaches until you find what works best for your site.